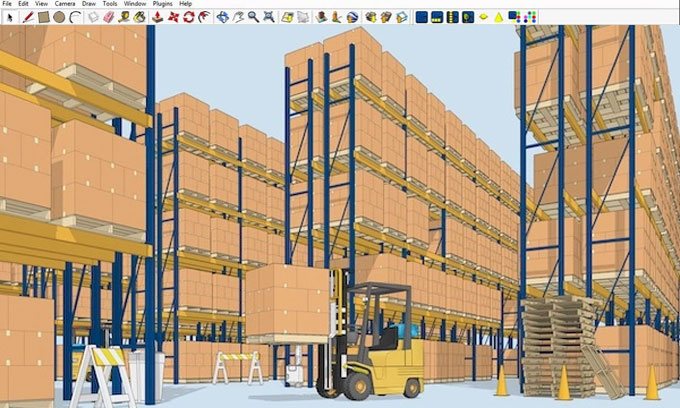
Visualizing and Building Automated Systems with SketchUp

In the fast-paced world of logistics and supply chain management, the demand for efficient and automated warehouse systems has never been higher. As businesses strive to meet the challenges of e-commerce, globalization, and consumer expectations, the role of advanced technology in warehouse design cannot be overstated.
One such technology that is gaining traction in the industry is SketchUp, a powerful 3D modeling software that goes beyond traditional design approaches to visualize and build automated warehouse systems.
The Evolution of Warehouse Design
Traditionally, warehouse design involved complex blueprints and 2D layouts that often left much to the imagination. As the need for more sophisticated and dynamic warehouse solutions emerged, the industry began to transition towards 3D modeling.
This evolution not only improved the design process but also enhanced communication among stakeholders. SketchUp, with its intuitive interface and powerful features, has become a game-changer in this evolution, allowing designers and engineers to visualize warehouses in three dimensions and explore automated systems in a virtual environment before implementation.
The Power of SketchUp in Warehouse Design
A. User-Friendly Interface:
One of the key strengths of SketchUp is its user-friendly interface, making it accessible to both seasoned designers and newcomers to 3D modeling. The simplicity of SketchUp's tools empowers warehouse designers to create accurate and detailed models with ease. This user-friendliness not only expedites the design process but also promotes collaboration among multidisciplinary teams involved in warehouse projects.
B. 3D Visualization for Enhanced Decision-Making:
SketchUp's 3D modeling capabilities provide a realistic and immersive experience for warehouse designers.
With the ability to navigate and explore a virtual representation of the warehouse, stakeholders can make informed decisions about layout, equipment placement, and workflow optimization. This visualization aspect is particularly crucial in the context of automated warehouse systems, where precision and efficiency are paramount.
C. Dynamic Components for Automation Simulation:
SketchUp's dynamic components feature allows designers to create intelligent and interactive elements within their models.
This functionality is instrumental in simulating the behavior of automated systems. For instance, conveyor belts, robotic arms, and automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) can be modeled as dynamic components, enabling designers to test and optimize their functionality before the physical implementation.
Applications of SketchUp in Automated Warehouse Design
A. Layout Planning and Optimization:
Efficient warehouse design starts with a well-thought-out layout that maximizes space utilization and minimizes bottlenecks. SketchUp excels in creating detailed layouts, allowing designers to experiment with different configurations to find the most optimal solution.
This is especially critical in the context of automated systems, where the seamless integration of robotic movements and conveyor systems is paramount.
B. Simulation of Automated Processes:
SketchUp's dynamic components and animation features enable designers to simulate automated processes within the warehouse. This includes the movement of robots, sorting systems, and other automated machinery.
By visualizing these processes in a virtual environment, designers can identify potential issues, optimize workflows, and ensure the smooth operation of the automated system once implemented.
C. Collaborative Design and Stakeholder Communication:
Warehouse projects involve collaboration among various stakeholders, including architects, engineers, logistics experts, and facility managers.
SketchUp's cloud-based collaboration features facilitate real-time communication and feedback, allowing all stakeholders to actively participate in the design process. This ensures that the final warehouse design meets the requirements and expectations of everyone involved.
Case Studies: SketchUp in Action
To better illustrate the practical application of SketchUp in automated warehouse design, let's explore two hypothetical case studies.
A. Case Study 1: Robotics Integration:
Imagine a warehouse seeking to implement a robotic picking system to enhance order fulfillment speed and accuracy. With SketchUp, designers can create a 3D model of the warehouse and integrate dynamic components representing the robotic arms and their movements.
By simulating the picking process in the virtual environment, designers can fine-tune the placement of robots, optimize their paths, and identify potential collision points. This ensures a seamless integration of the robotic system into the existing warehouse layout.
B. Case Study 2: AS/RS Implementation:
In another scenario, a distribution center aims to implement an Automated Storage and Retrieval System (AS/RS) to streamline inventory management. SketchUp allows designers to model the AS/RS components, such as vertical storage racks and robotic shuttles.
The dynamic components feature enables designers to simulate the retrieval of products from the storage system, ensuring that the AS/RS operates efficiently and interfaces smoothly with other warehouse processes. This level of simulation and visualization is invaluable in avoiding costly errors during the implementation phase.
Overcoming Challenges with SketchUp
While SketchUp offers a versatile platform for warehouse design, it's essential to acknowledge and address potential challenges.
A. Learning Curve:
Although SketchUp is known for its user-friendly interface, there may be a learning curve for those new to 3D modeling. To overcome this challenge, training programs and tutorials can be implemented to familiarize warehouse designers with the software's functionalities.
B. Scaling Complexity:
As warehouse designs become more complex, especially with the integration of advanced automation systems, the scalability of SketchUp may pose a challenge. To address this, designers can leverage plugins and extensions that enhance SketchUp's capabilities, allowing it to handle larger and more intricate models.
Future Trends and Innovations
As technology continues to advance, the future of warehouse design with SketchUp looks promising. Emerging trends such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) integration could further enhance the design and simulation experience. Imagine walking through a virtual representation of a warehouse, experiencing automated processes in real-time, and making design decisions in an immersive 3D environment.
Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms within SketchUp could provide predictive analytics for warehouse performance.
To learn more, watch the following video tutorial.
Video Source: WarehouseBlueprint
Designers could simulate various scenarios and receive insights into the most efficient layout and automation configurations based on historical data and real-time simulations.
Conclusion:
In the ever-evolving landscape of warehouse design, SketchUp stands out as a powerful tool for visualizing and building automated systems. Its user-friendly interface, 3D modeling capabilities, and dynamic components feature make it an invaluable asset for warehouse designers seeking to create efficient, automated solutions.
Through case studies and an exploration of its applications, we've seen how SketchUp can revolutionize the way warehouses are designed and optimized.
As we look to the future, the integration of emerging technologies like AR, VR, and AI holds the potential to take warehouse design to new heights. With SketchUp at the forefront, the industry can continue to innovate and meet the challenges of a rapidly changing global market. Whether you are a seasoned warehouse designer or a newcomer to the field, embracing SketchUp can pave the way for more efficient, automated, and future-ready warehouse systems.